This post contains affiliate links, and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my links. Thanks in advance! I honestly hope this content makes you want to click the links to gain more knowledge.
The paste command is the topic of a video I made a while back. In it, I demonstrate how to use the paste command to concatenate a string of different values.
That video is fine, but the real power in the paste command in my opinion is its ability to assemble strings as labels for plots and reports
Imagine you have a graph with a line on it, and you want to label the graph with the slope of the line, or with the correlation coefficient. This will change with the underlying data, so you want a label that provides you a refreshable variable.
The Paste Command Basic Syntax
As you probably know by now, when you run equations in R code in R GUI, the answer prints to the console. If you want to keep the result of the equation for the future, you have to store them in a named object, and use the arrow command.
And as you probably already also know by now, storing results in objects in R and then calling them up later makes your life easier when you are not very good at programming, like me. As an example, in this blog post, I show you how to save different hexadecimal color codes as a string called cool_colors, and then use that string while making a plot so that you can overwrite the default colors with the cool colors!
So the paste() command is basically your hack for storing report and plot labels with values in them from your data, and then calling up the label later in your report or plot (or both! It’s recyclable!). First, let’s just look at some simple paste() code from my other video (available on Github).
Let’s start by looking at code that creates an object called PhoneNumber through pasting a few numeric sequences together (three arguments in total), followed by the sep=”” argument, which always comes at the end of paste(). The sep=”” option tells R to put “nothing” between each argument.
PhoneNumber <- paste(612,781,8888,sep="")
So as you can guess, when I run this code, you will get an object called PhoneNumber. If you run that object, the value of it will be 6127818888.
The Paste Command for Refreshable Labels for Plots and Reports
In my example above, all those arguments are hardcoded into the paste() string. Now, let’s shift our thinking to ways we can include arguments that are results of calculations done on the data – such as a correlation coefficient, as I mentioned earlier! We basically could run that calculation, and put it in the string as part of a label. If we save that string as an object, then we can call up and reuse that object as a label on plots and reports.
In my tutorial video on the topic, I show an example of taking a dataset called lineitems with a numeric variable called Tot_Cost (meaning “total cost”) and finding the maximum value of the column by doing max(lineitems$Tot_Cost). Then, I include the code below to create a label for a report.
report_label <- paste("The maximum total cost is ", max(lineitems$Tot_Cost),
"!!!!", sep="")
As you can see, the code makes the object called report_label, and includes the calculation as the second argument. See how the string comes out when I run report_label to the console:
"The maximum total cost is 293.88!!!!"
Updated October 12, 2022. Revised banners and updated June 16, 2023.
Read all of our data science blog posts!
Confidence Intervals are for Estimating a Range for the True Population-level Measure
Confidence intervals (CIs) help you get a solid estimate for the true population measure. Read [...]
1 Comment
Jun
Continuous Variable? You Can Categorize it!
Continuous variable categorized can open up a world of possibilities for analysis. Read about it [...]
184 Comments
Jun
Delete if the Row Meets Criteria? Do it in SAS!
Delete if rows meet a certain criteria is a common approach to paring down a [...]
May
Chi-square Test: Insight from Using Microsoft Excel
Chi-square test is hard to grasp – but doing it in Microsoft Excel can give [...]
May
Identify Elements of Research in Scientific Literature
Identify elements in research reports, and you’ll be able to understand them much more easily. [...]
May
Design the Most Useful Time Periods for Your Conversions
Time periods are important when creating a time series visualization that actually speaks to you! [...]
Apr
Apply Weights? It’s Easy in R with the Survey Package!
Apply weights to get weighted proportions and counts! Read my blog post to learn how [...]
Nov
Make Categorical Variable Out of Continuous Variable
Make categorical variables by cutting up continuous ones. But where to put the boundaries? Get [...]
Nov
Remove Rows in R with the Subset Command
Remove rows by criteria is a common ETL operation – and my blog post shows [...]
Oct
CDC Wonder for Studying Vaccine Adverse Events: The Shameful State of US Open Government Data
CDC Wonder is an online query portal that serves as a gateway to many government [...]
Jun
AI Careers: Riding the Bubble
AI careers are not easy to navigate. Read my blog post for foolproof advice for [...]
Jun
Descriptive Analysis of Black Friday Death Count Database: Creative Classification
Descriptive analysis of Black Friday Death Count Database provides an example of how creative classification [...]
Nov
Classification Crosswalks: Strategies in Data Transformation
Classification crosswalks are easy to make, and can help you reduce cardinality in categorical variables, [...]
Nov
FAERS Data: Getting Creative with an Adverse Event Surveillance Dashboard
FAERS data are like any post-market surveillance pharmacy data – notoriously messy. But if you [...]
4 Comments
Nov
Dataset Source Documentation: Necessary for Data Science Projects with Multiple Data Sources
Dataset source documentation is good to keep when you are doing an analysis with data [...]
Nov
Joins in Base R: Alternative to SQL-like dplyr
Joins in base R must be executed properly or you will lose data. Read my [...]
Nov
NHANES Data: Pitfalls, Pranks, Possibilities, and Practical Advice
NHANES data piqued your interest? It’s not all sunshine and roses. Read my blog post [...]
Nov
Color in Visualizations: Using it to its Full Communicative Advantage
Color in visualizations of data curation and other data science documentation can be used to [...]
Oct
Defaults in PowerPoint: Setting Them Up for Data Visualizations
Defaults in PowerPoint are set up for slides – not data visualizations. Read my blog [...]
Oct
Text and Arrows in Dataviz Can Greatly Improve Understanding
Text and arrows in dataviz, if used wisely, can help your audience understand something very [...]
Oct
Shapes and Images in Dataviz: Making Choices for Optimal Communication
Shapes and images in dataviz, if chosen wisely, can greatly enhance the communicative value of [...]
Oct
Table Editing in R is Easy! Here Are a Few Tricks…
Table editing in R is easier than in SAS, because you can refer to columns, [...]
Aug
R for Logistic Regression: Example from Epidemiology and Biostatistics
R for logistic regression in health data analytics is a reasonable choice, if you know [...]
272 Comments
Aug
Connecting SAS to Other Applications: Different Strategies
Connecting SAS to other applications is often necessary, and there are many ways to do [...]
Jul
Portfolio Project Examples for Independent Data Science Projects
Portfolio project examples are sometimes needed for newbies in data science who are looking to [...]
Jul
Project Management Terminology for Public Health Data Scientists
Project management terminology is often used around epidemiologists, biostatisticians, and health data scientists, and it’s [...]
Jun
Rapid Application Development Public Health Style
“Rapid application development” (RAD) refers to an approach to designing and developing computer applications. In [...]
Jun
Understanding Legacy Data in a Relational World
Understanding legacy data is necessary if you want to analyze datasets that are extracted from [...]
Jun
Front-end Decisions Impact Back-end Data (and Your Data Science Experience!)
Front-end decisions are made when applications are designed. They are even made when you design [...]
Jun
Reducing Query Cost (and Making Better Use of Your Time)
Reducing query cost is especially important in SAS – but do you know how to [...]
Jun
Curated Datasets: Great for Data Science Portfolio Projects!
Curated datasets are useful to know about if you want to do a data science [...]
May
Statistics Trivia for Data Scientists
Statistics trivia for data scientists will refresh your memory from the courses you’ve taken – [...]
Apr
Management Tips for Data Scientists
Management tips for data scientists can be used by anyone – at work and in [...]
Mar
REDCap Mess: How it Got There, and How to Clean it Up
REDCap mess happens often in research shops, and it’s an analysis showstopper! Read my blog [...]
Mar
GitHub Beginners in Data Science: Here’s an Easy Way to Start!
GitHub beginners – even in data science – often feel intimidated when starting their GitHub [...]
Feb
ETL Pipeline Documentation: Here are my Tips and Tricks!
ETL pipeline documentation is great for team communication as well as data stewardship! Read my [...]
Feb
Benchmarking Runtime is Different in SAS Compared to Other Programs
Benchmarking runtime is different in SAS compared to other programs, where you have to request [...]
Dec
End-to-End AI Pipelines: Can Academics Be Taught How to Do Them?
End-to-end AI pipelines are being created routinely in industry, and one complaint is that academics [...]
Nov
Referring to Columns in R by Name Rather than Number has Pros and Cons
Referring to columns in R can be done using both number and field name syntax. [...]
Oct
The Paste Command in R is Great for Labels on Plots and Reports
The paste command in R is used to concatenate strings. You can leverage the paste [...]
Oct
Coloring Plots in R using Hexadecimal Codes Makes Them Fabulous!
Recoloring plots in R? Want to learn how to use an image to inspire R [...]
5 Comments
Oct
Adding Error Bars to ggplot2 Plots Can be Made Easy Through Dataframe Structure
Adding error bars to ggplot2 in R plots is easiest if you include the width [...]
Oct
AI on the Edge: What it is, and Data Storage Challenges it Poses
“AI on the edge” was a new term for me that I learned from Marc [...]
Jun
Pie Chart ggplot Style is Surprisingly Hard! Here’s How I Did it
Pie chart ggplot style is surprisingly hard to make, mainly because ggplot2 did not give [...]
5 Comments
Apr
Time Series Plots in R Using ggplot2 Are Ultimately Customizable
Time series plots in R are totally customizable using the ggplot2 package, and can come [...]
Apr
Data Curation Solution to Confusing Options in R Package UpSetR
Data curation solution that I posted recently with my blog post showing how to do [...]
Apr
Making Upset Plots with R Package UpSetR Helps Visualize Patterns of Attributes
Making upset plots with R package UpSetR is an easy way to visualize patterns of [...]
11 Comments
Apr
Making Box Plots Different Ways is Easy in R!
Making box plots in R affords you many different approaches and features. My blog post [...]
Mar
Convert CSV to RDS When Using R for Easier Data Handling
Convert CSV to RDS is what you want to do if you are working with [...]
Mar
GPower Case Example Shows How to Calculate and Document Sample Size
GPower case example shows a use-case where we needed to select an outcome measure for [...]
Feb
Querying the GHDx Database: Demonstration and Review of Application
Querying the GHDx database is challenging because of its difficult user interface, but mastering it [...]
Feb
Variable Names in SAS and R Have Different Restrictions and Rules
Variable names in SAS and R are subject to different “rules and regulations”, and these [...]
Feb
Referring to Variables in Processing Data is Different in SAS Compared to R
Referring to variables in processing is different conceptually when thinking about SAS compared to R. [...]
Jan
Counting Rows in SAS and R Use Totally Different Strategies
Counting rows in SAS and R is approached differently, because the two programs process data [...]
Jan
Native Formats in SAS and R for Data Are Different: Here’s How!
Native formats in SAS and R of data objects have different qualities – and there [...]
Jan
SAS-R Integration Example: Transform in R, Analyze in SAS!
Looking for a SAS-R integration example that uses the best of both worlds? I show [...]
Dec
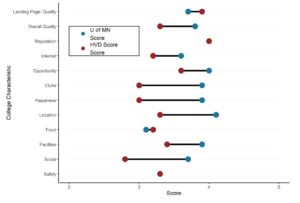
Dumbbell Plot for Comparison of Rated Items: Which is Rated More Highly – Harvard or the U of MN?
Want to compare multiple rankings on two competing items – like hotels, restaurants, or colleges? [...]
2 Comments
Sep
Data for Meta-analysis Need to be Prepared a Certain Way – Here’s How
Getting data for meta-analysis together can be challenging, so I walk you through the simple [...]
Jul
Sort Order, Formats, and Operators: A Tour of The SAS Documentation Page
Get to know three of my favorite SAS documentation pages: the one with sort order, [...]
Nov
Confused when Downloading BRFSS Data? Here is a Guide
I use the datasets from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance Survey (BRFSS) to demonstrate in [...]
2 Comments
Oct
Doing Surveys? Try my R Likert Plot Data Hack!
I love the Likert package in R, and use it often to visualize data. The [...]
3 Comments
Oct
I Used the R Package EpiCurve to Make an Epidemiologic Curve. Here’s How It Turned Out.
With all this talk about “flattening the curve” of the coronavirus, I thought I would [...]
Mar
Which Independent Variables Belong in a Regression Equation? We Don’t All Agree, But Here’s What I Do.
During my failed attempt to get a PhD from the University of South Florida, my [...]
Aug
The paste command in R is used to concatenate strings. You can leverage the paste command to make refreshable label objects for reports and plots, as I describe in my blog post.